OsteoarthritisIt is a chronic non-inflammatory disease of joints or articular cartilage and surrounding tissues. Osteoarthritis is one of the most common diseases affecting 10-14% of the world's population. Basically, this disease affects women between 45 and 55 years old. Osteoarthritis is the most common joint disease, accounting for nearly 80% of all joint causes.
The cause of this disease is currently unclear.. . . All the factors that cause tissue degeneration and aging will lead to the occurrence of this disease. Therefore, with age, the appearance of osteoarthritis is almost inevitable.
The occurrence of this disease has external and internal causes.The main external factors of osteoarthritis include humidity, hypothermia, unfavorable working conditions, overloaded joints with frequent microtrauma, and exposure to radiant energy and vibration. The main and fairly common cause of osteoarthritis is the inability of cartilage to resist the increased pressure on the joints. The reasons for this performance may be impaired posture, long-term work, standing, or even some sports: weightlifting, running or jumping.
The internal factors leading to this disease include the occurrence of hereditary cartilage tissue diseases, impaired blood supply to joints, hormonal imbalance and metabolic disorders. The cause of female osteoarthritis may be menopausal ovarian dysfunction. In addition, the early development of atherosclerosis may also be the cause of this disease.
Osteoarthritis can also be secondary to diseases such as congenital dislocation, rheumatoid arthritis, intra-articular fractures, and even alcoholism.
What are the symptoms and clinical signs of this disease?
Osteoarthritis is manifested by severe joint pain and deformation, leading to violations of its function. For this disease, the most common injuries are weight-bearing joints (hip and knee joints) and small joints of the hand. The spine is also involved in this process. But the most common is that the knee and hip joints are affected.
The most basic symptomsWith osteoarthritis, severe pain can occur in the affected joint area. These pains can cause damage to the bones, joints, or tissues around the joints. Usually, this pain increases with fatigue, and decreases during rest. Pain at night, swelling of the joints, and a "sticky feeling of gel" in the affected joints in the morning-all of these indicate the occurrence of osteoarthritis. The intensity of this pain depends on multiple causes (atmospheric pressure, humidity, and temperature changes). All these factors begin to affect the pressure in the joint cavity, which leads to these pains.
The next major symptom of osteoarthritis is the creaking or squeaking of joints, not only when walking, but even during any exercise. The appearance of this kind of squeaking or squeaking sound is related to the invasion of the joint surface, which will cause the movement of the joint to be restricted.
With osteoarthritis, the joint volume increases, which is the result of edema in the tissues around the joint. Swelling or fever in affected joints is extremely rare.
Clinical forms of osteoarthritis:
- arthritis.
- Hip joint disease.
- Osteoarthritis of the interphalangeal joint of the distal hand.
- Osteoarthritis of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the hand.
- Deformable spondylopathy.
- Intervertebral osteochondrosis.
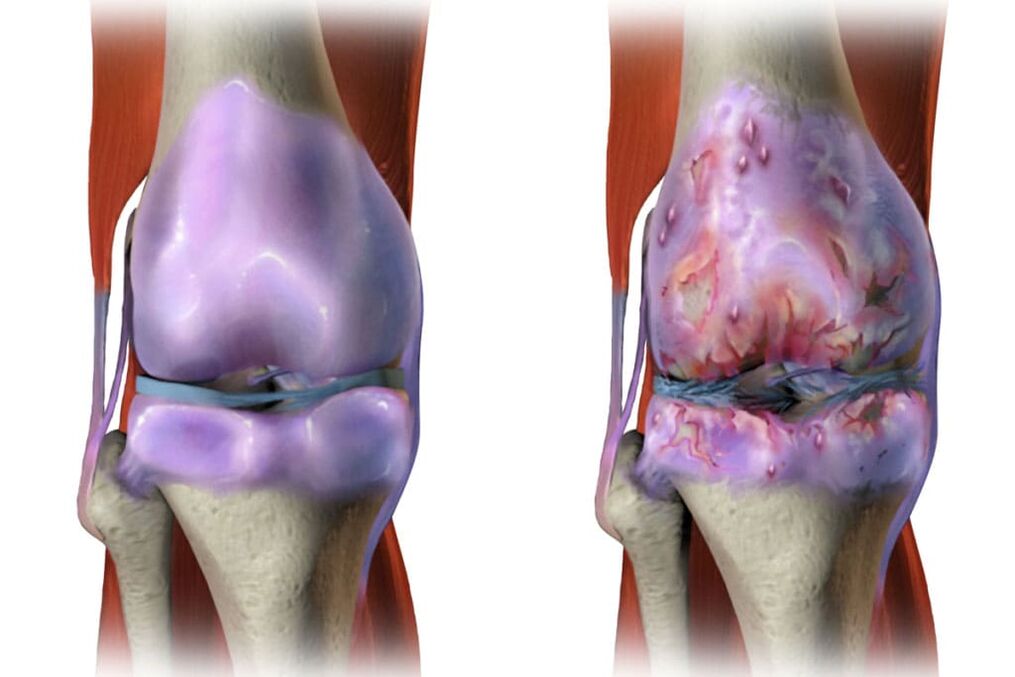
Knee joint diseaseIt is a lesion of the knee joint in osteoarthritis. In this case, the knee joint pain will appear when walking, especially when going down the stairs. The location of these pains is the inside and front of the affected knee joint. When the knee is bent, the discomfort increases. In addition, in many cases of knee arthropathy, the knee joint will be deviated. The disease started gradually, and the pain became more and more severe. Through active and passive movement, a creaking sound can be heard. The pain starts to get worse, and in many cases it progresses to synovitis-inflammation of the capsule of the joint or tendon.
Hip joint disease-This is a lesion of the hip joint. The initial pain of a hip injury does not appear in the thigh area, but in the knee, groin, or buttocks. They increase with walking and subside at rest. These pains occur even with small changes in X-rays and are related to muscle cramps. With the failure of the hip joint, the limitation of joint range of motion gradually increases. This disease is the result of trauma or arthritis. Patients with hip joint disease will have a "duck" gait, lameness, and hip and thigh muscle atrophy. In addition, there is pain on palpation in the femoral head area.
Osteoarthritis or Heberden's tubercle of the interphalangeal joint of the distal hand. . . The appearance of this nodule is most common in menopausal women. Initially, they appeared on the first and third fingers of the hand. Over time, that is, months or even years later, symmetrical lesions are observed in other distal interphalangeal joints. This nodule is located on the dorsolateral surface of the joint.
Osteoarthritis of the proximal interphalangeal joint or Bouchard's tubercle of the hand.Unlike Heberden nodules, these nodules appear on the side of the joint, causing the joint to expand laterally. As a result of this increase, the fingers acquire a fusiform shape.
Deformable spondylopathy-Due to this disease in the vertebral area, marginal bone growth occurs. This disease began to appear at the age of 20. Osteophytes (bone growth) look like swelling-edema due to pressure on blood vessels. As a result, stiffness of the spine occurs and, in some cases, neurological diseases.
Intervertebral osteochondrosisOccurs in combination with spinal curvature or deformable spondylosis. For this disease, the intervertebral disc degenerates and the nucleus pulposus protrudes in different directions, which can lead to spinal trauma. There is also excessive growth of osteophytes and increased joint surface. In this case, the choroid of the joints is affected, so vasculitis-inflammation of the walls of small blood vessels occurs. The pain syndrome is very obvious and worsens with physical exertion or hypothermia.
There are two main forms of osteoarthritis-It is primary or idiopathic (the cause of the disease has not been clarified) and secondary (the disease occurs in the context of other diseases).
Primary osteoarthritisWhen less than 3 joints are affected, it is localized. Localized osteoarthritis can affect the spine, hand and foot joints, knee joints, hip joints and other joints.
Systemic osteoarthritis can also occur when 3 or more joints are affected. In this case, the large joints and the distal interphalangeal joints are affected. In addition, in the broadest form, erosive osteoarthritis can also occur.
Secondary osteoarthritisIt can be post-traumatic. In addition, the cause of secondary osteoarthritis may be metabolic diseases, such as genetic disease Gaucher disease; Wilson’s disease is a rare liver injury in which copper metabolism is impaired; hemochromatosis, or also known as bronzeDiabetes mellitus or pigmented liver cirrhosis is a genetic disease in which iron metabolism is disordered and accumulated in organs and tissues. Diseases such as diabetes, hypothyroidism (hypothyroidism), and acromegaly (hypertrophic growth hormone) may also be the cause of osteoarthritis. In addition to these diseases, osteoarthritis can also cause many diseases such as calcium deposition disease and neuropathy.
What happens to osteoarthritis?
For this disease, articular cartilage will undergo severe aging. As a result, the articular cartilage loses its elasticity. In addition to the surface of the joints becoming rough, cracks still appear on them. In many cases, the cartilage is worn away enough to expose the bones. All of these will cause the elasticity of the articular cartilage to decrease and cause the joint to rupture. In addition, inflammation can join all of the listed changes, whereby the growth of bone tissue occurs, which leads to joint disease and deformation.
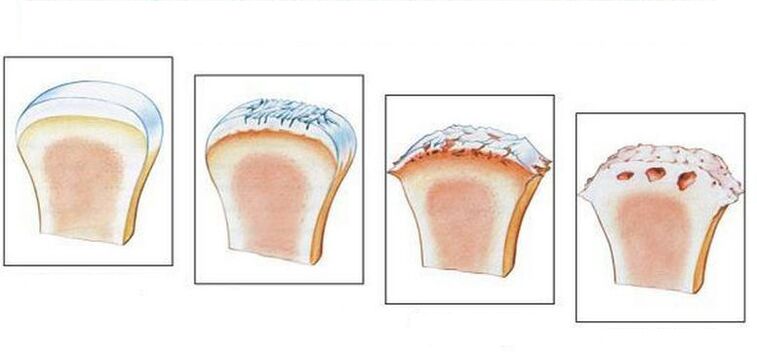
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
In many cases, the diagnosis of osteoarthritis does not cause much difficulty. But there are exceptions, such as patients with shoulder joint disease and symptoms of joint inflammation. Diagnosis of primary and secondary osteoarthritis may also be difficult, and its occurrence is related to metabolism or other diseases. In the X-ray examination, if there are clinical signs of osteoarthritis, the signs of osteoarthritis (especially the elderly) can be quickly detected. In order to make a final diagnosis, there is not enough X-ray and laboratory data. For this reason, it is necessary to conduct some additional research to determine the exact cause of joint pain.
Osteoarthritis treatment
In order to reduce or completely suppress pain, there are two methods, drug and non-drug, including physical therapy and exercise therapy. In order to prescribe the correct treatment plan, a separate approach is required for each patient. In this case, the individual characteristics of the patient and the particularity of the disease process must be considered.
When treating osteoarthritis, we must first observe the medication plan, because mechanical unloading of joints is not only the main factor in reducing pain, but also plays an important role in the treatment of this disease. In this case, it is necessary to rule out a long stay in a fixed position, long walking and standing on both legs, and rule out weight transfer that may cause mechanical overload of the joints. If the disease is neglected, it is recommended that the patient walk on crutches or canes. Due to the considerable pain as the disease worsens, some patients are prescribed a semi-recumbent regimen.
During the treatment of osteoarthritis, it is recommended to follow a diet to reduce excess weight. This is especially true for people with knee injuries.
In addition, in the treatment of this disease, the physical therapy used can not only reduce pain and inflammation, but also have a positive effect on the metabolic process of joint tissues and improve microcirculation. Physiotherapy involves the use of electric current, alternating magnetic current, electrophoresis, and ultraviolet radiation and sonication on the affected joints. In addition, thermal procedures, the use of peat mud and paraffin wax are also specified.
Using therapeutic massage elements, patients should try to avoid mechanical stimulation of the joint capsule. Only in this case, the painful muscle spasm is reduced, and the weakened muscle tension also increases, so the patient's functional ability is improved.
Drug treatment depends on the form of the disease and the severity of the course. In more severe cases, the patient receives surgical treatment (arthroplasty).
In addition, patients are advised to take spa treatments at the seaside.
Prevent osteoarthritisIncluding daily special exercises that help strengthen muscle and ligament devices. Getting rid of excess weight, limiting weight, and adding jelly, aspic or aspic and other dishes to the menu are all measures to prevent osteoarthritis. And, of course, participate in sports like swimming. It must be remembered that preventing any disease is better than curing. The same applies to diseases such as osteoarthritis. In order not to think about how to get rid of the severe pain of osteoarthritis and how to cure this disease in the future, it is necessary to take preventive measures today rather than postpone it until later.
Various methods to treat osteoarthritis deformans
Highly educated and accumulated experience in the use of shock wave therapy can achieve the maximum positive therapeutic effect even in the late stage of the disease, avoiding surgical treatment in many cases.
Shockwave therapy is performed on modern equipment:
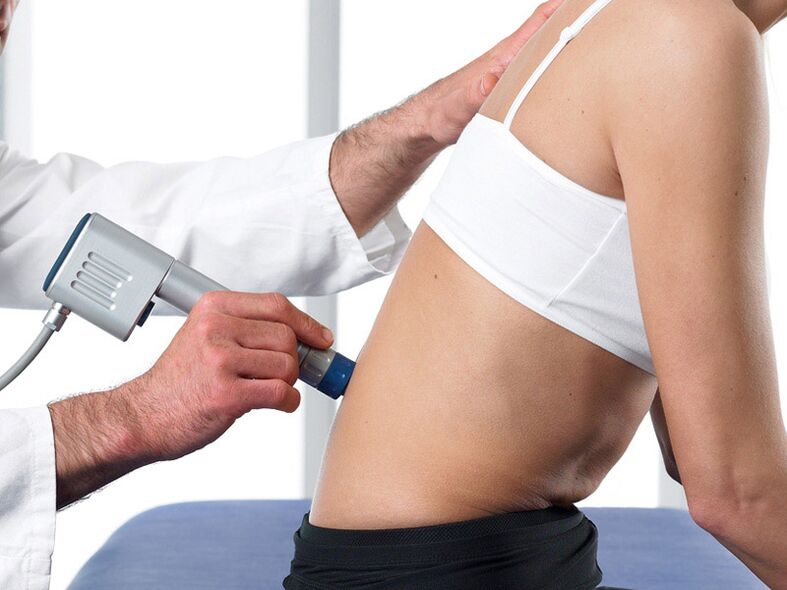

- The process of using UHT method to treat arthritis and joint disease includes 5-7 courses;
- The meeting will be held once within 5-7 days.
Under the influence of the shock wave, the calcium salt crystallites and fibrotic areas formed in the joint tissue loosen in the affected tissue. At the same time, blood flow in damaged tissues increases tenfold, which helps reabsorption of calcium salts and fibrotic areas.
Advantages of the SWT method:
- efficient;
- Good tolerance (no need to use anesthesia);
- Reduce the need for other methods, especially surgical treatment;
- Quickly relieve pain without analgesics;
- The possibility of use in the chronic stage of the disease and its main manifestations;
- It is carried out in an outpatient clinic, without hospitalization, and will not disrupt the patient's normal rhythm of life.
Orthopedic Photodynamic TherapyIt is a non-invasive, non-complicated two-component treatment method. To implement this method, a photosensitizer and a laser radiation source with a wavelength of 660-670 nm approved for medical use are used.
Under the influence of the laser beam, the photosensitizer is excited to release singlet oxygen, which has a toxic effect on the cell's energy complex (mitochondria and Golgi complex), destroys the latter, and triggers an irreversible apoptosis process. At the same time, healthy cells will not be damaged. The damaged pathological tissue is aseptically absorbed.
The photosensitizer is injected into the patient through the skin (application).
PRP plasma boost-This plastic surgery operation is based on a patented method of processing patient blood using special vacuum biotechnology tubes and special centrifugal mode.
During the operation, an injected form of autologous plasma containing platelets is separated from the patient's blood, and then injected into the soft tissues around the joints and directly into the joint cavity of the patient. Autologous injection can reduce inflammation, relieve pain and restore the range of motion of the joint. Autologous treatment procedures minimize the number of drugs used or eliminate them completely, thereby reducing the toxic effects of the drugs on the patient's body. In addition, autologous injection can help reduce the treatment time by 2-3 times.
Surgical indications (PRP plasma lift):
- Osteoarthritis;
- Osteoarthritis;
- arthritis;
- Tendinopathy,
- Damage to ligaments and muscles.
Therefore, shock wave therapy, photodynamic therapy and plasma lift (PRP) in orthopedics are the best options for treating joint diseases. They can allow you to achieve positive results through the use of modern equipment and technology, as well as the experience of doctors.


















































